
If PC1 and PC2 are not able to connect each other and if you are not able to share resources of VLAN 20 from VLAN 10 and Vice versa. Troubleshooting Inter-VLAN Routing Configuration Virtual LAN ID: 20 (Inter Switch Link Encapsulation) Protocols Configured: Address: Received: Transmitted: Virtual LAN ID: 10 (Inter Switch Link Encapsulation) Ping PC2 from PC1 to check if both the PCs in different VLANs can connect to each other. Interface Subinterface Gateway IP Address/Mask VLAN ID Router Encapsulationįa0/0 fa0/0.10 192.168.1.1/24 VLAN 10 encapsulation dot1q 10įa0/0 fa0/0.20 192.168.2.1/24 VLAN 20 encapsulation dot1q 20 View the router configuration using the show running-config command in privileged EXEC mode to verify the router configuration.
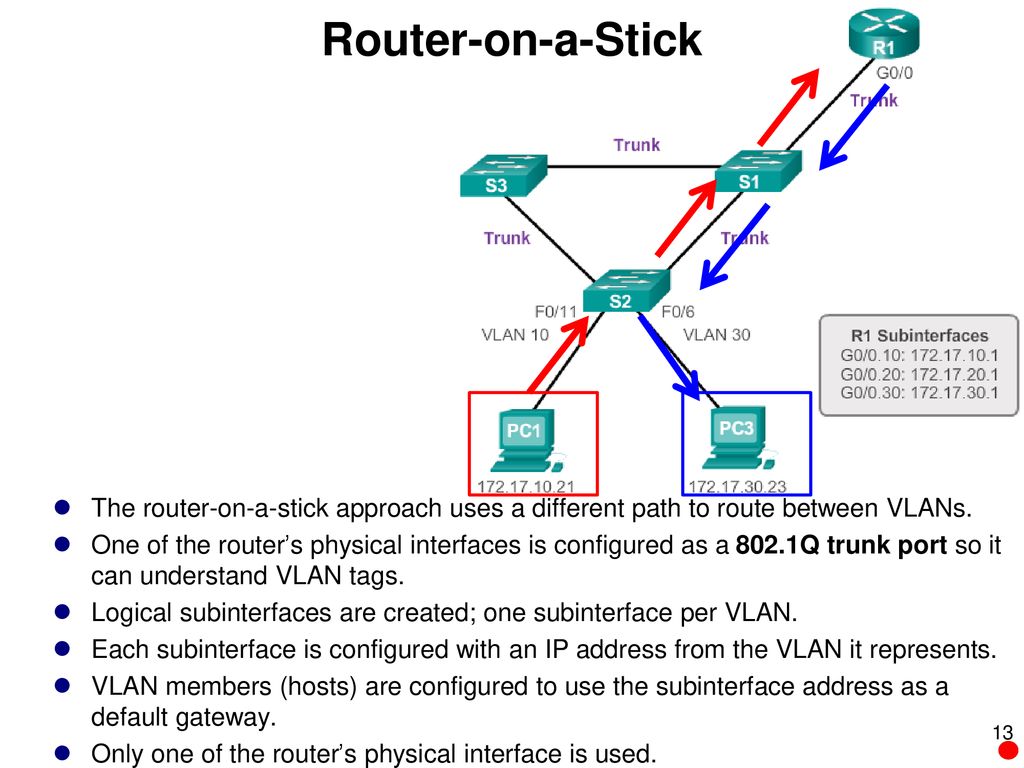
You also need to configure the router with the default gateways that you have configured on the PC1 and PC2 and assign IP address to the sub interfaces if the router. Next, assign VLAN ID using the encapsulation dot1q vlan_id subinterface. Use interface interface_id.Subinterface_id command to create sub interfaces. Remember, you cannot use the switchport mode dynamic auto or switchport mode dynamic desirable modes to create trunk on the router because the routers do not support dynamic trunking protocol.Ĭonfigure PC1 and PC2 with IP addresses and the default gatewaysĪt this stage if you try to check the connectivity between PC1 and PC2, the connectivity will fail because the router that would connect the two VLANs is not configured,Ĭonfigure router with IP addresses to perform the inter-VLAN routingso that the router can route frames between VLAN 10 and VLAN 20. PC1 and PC2 are connected to VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 respectively. VLANs 10 and 20 have also been added to switch SW1. The Router R1 is connected to switch SW1 on trunk port F0/3. Let us configure the setup shown in the diagram given below. The router may use routing table to forward data to the correct device, if the destination address is on adifferent VLAN. To do this, you need to configure IP addresses on the router interfaces, which would be used by computers on VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 to accessthe devices connected to each other.

The router will accept the tagged VLAN traffic on its trunk interface and route traffic between different VLANs. Let us create a Router on stick setup where a single router interface is configured as a trunk link. To configure Router on stick inter-VLAN mechanism,you need to configure the router’s interfaces as trunk links. You can configure multiple VLANs on a single interface using Router on stick inter-VLAN mechanism. In this setup, you are configuring each VLAN on a separate router interface.
ROUTER ON A STICK CONFIGURATION PC
Also, PC 1 is configured on VLAN 10 and PC 2 is configured on VLAN 20.
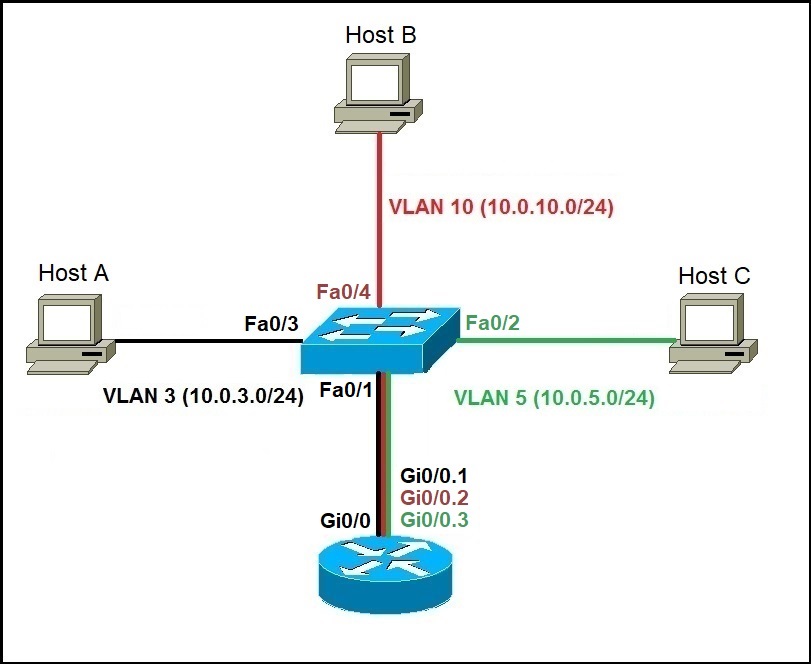
The switch ports Fa0/4 and Fa0/3, which are also the part of VLANs 10 and 20 respectively, are configured to router interfaces. The Switch SW1 has two VLANs VLAN 10 and VLAN 20 configured on interfacesFa/08 and Fa0/11 respectively. The following figure explains the scenario. The router accepts traffic on its interface from one VLAN through switch and routes the traffic to another VLAN. In a traditional inter-VLAN routing setup, each router interface is connected to a separate network through a switch port, which is also associated with a specific VLAN. To allow communication between different VLANs you can configure inter-VLAN routing between them.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
